
By Linda J. Blumberg, Kevin Lucia, and Kennah Watts
The excessive price of well being care is entrance of thoughts for many American voters this election cycle, and policymakers throughout the political spectrum have floated reforms to convey down well being care prices. Nevertheless, figuring out and advancing insurance policies that really ship inexpensive, top quality well being care requires policymakers, researchers, and different stakeholder to grasp how the well being care system has turn into more and more financially intertwined and riddled with incentives that drive prices ever larger, typically at sufferers’ expense. Within the final quarter century, the well being care market has seen important vertical and horizontal integration of well being care suppliers and insurers, with appreciable analysis that evidences how this consolidation results in larger costs and decrease high quality of care.
Whereas these types of integration are very important to grasp and tackle, we should widen this consolidation image additional. The monetary pursuits of suppliers, insurers, administrative entities, and different “intermediary” companies are actually strongly aligned to extend well being care spending by means of a posh internet of widespread possession, contracting preparations, and monetary offers which create an array of conflicts of pursuits and hidden flows of cash. These strongly aligned pursuits and relationships collectively contribute to elevated well being care spending by means of a posh internet of widespread possession, contracting preparations, and monetary offers which create an array of conflicts of pursuits and hidden flows of cash (see Determine 1).
Determine 1. The Complicated Net: Illustrative Examples of Intertwined Monetary Pursuits
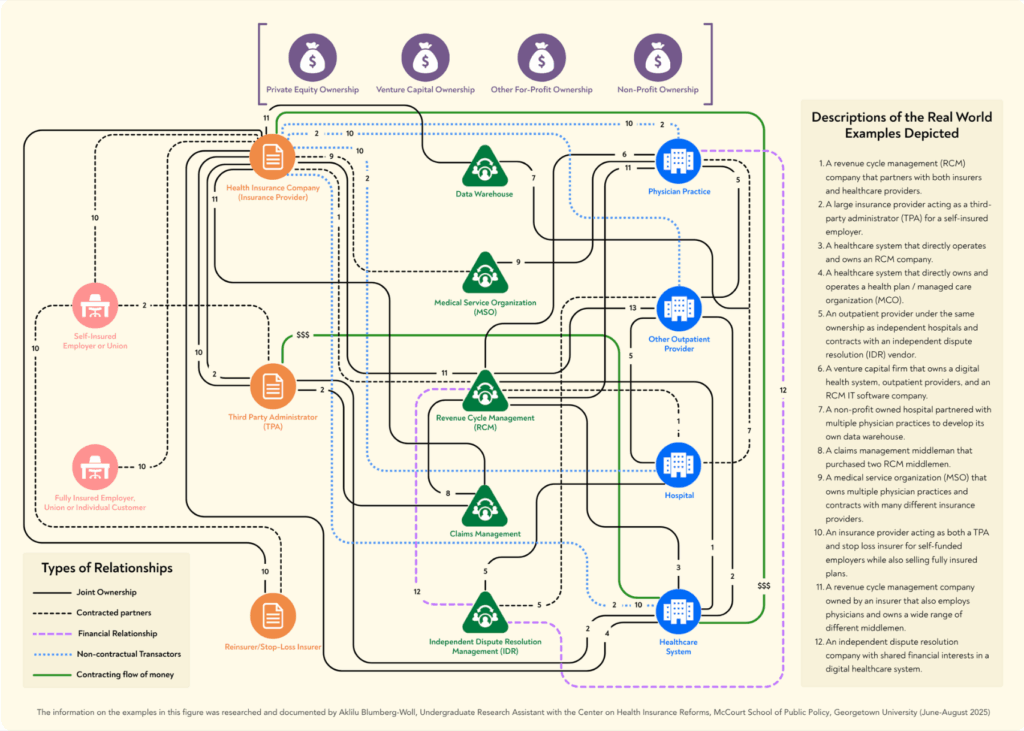
The complexity is so great that it’s nearly unimaginable to seize the complete image of the prevailing monetary relationships, and that’s the level––by means of opaque relationships and hidden practices, these entities function with out ample oversight or limits. Regardless of the challenges inherent in unwinding the parts of the online, it’s vital that we start to do an accounting of the present nature of our well being care eco-system to grasp its implications for personal and authorities spending on well being care, and, finally, entry to and high quality of care. A giant-picture understanding can also be vital for designing and selling public coverage approaches to rationalize well being care prices and promote entry to high-quality medical companies.
In a just lately printed skilled perspective, we dive into this case and display that the proliferation of administrative and monetary middlemen collaborating or entwined with insurers, TPAs, and/or suppliers, in addition to the interrelationships between insurers, TPAs, and suppliers themselves, all work towards an environment friendly market equilibrium and, as an alternative, inflate spending on well being care items and companies.
Right here we current a condensed model of this skilled perspective, which focuses on medical advantages and the marketplace for industrial insurance coverage.
Progress in Spending on Personal Well being Insurance coverage is Correlated with Progress in Administrative Prices and the Middlemen Market
Spending on non-public medical health insurance has grown significantly within the final decade. As whole expenditures on non-public medical health insurance greater than tripled from 2020 to 2023, so too did the online price of medical health insurance, also referred to as administrative prices ($150.78 billion in 2023). This administrative spending outpaced the expansion in non-public medical health insurance spending on doctor and clinic companies, retail medication, and all different bills collectively, apart from hospitals. Though a few of these administrative prices are essential to run a well being system, specialists posit that at least half of well being care administrative prices within the U.S. are wasteful.
This wasteful spending seems intently correlated to the scale and scale of well being care administrative and monetary middlemen, an trade that has skyrocketed in measurement in recent times. In 2024, the marketplace for just one kind of intermediary – income cycle administration (RCMs) corporations – was estimated at a worth of $172.24 billion, and it’s anticipated to develop by one other 10 % by 2030. The broader intermediary trade consists of, however is just not restricted to, RCMs, re-pricers, claims denial administration corporations, impartial dispute decision administration corporations, information warehouses, and level resolution distributors. Every of those middlemen revenue by growing income for insurers, suppliers, and typically each, and the charges paid to them add to supplier costs and/or the executive prices baked into non-public medical health insurance premiums.
Multifaceted Market Failures Underscore Why and How this Complicated Net has Arisen and Elevated Prices
A number of causes clarify how and why this internet has grown so entangled: suppliers dominate many markets, insurers and third-party directors (TPAs) have monetary pursuits to maintain spending excessive, and middlemen revenue from repeated adjudication of claims and different charges related to an ever extra complicated system. We discover every of those causes briefly beneath, and extra clarification and examples might be discovered within the full skilled perspective.
Many Suppliers Face No Constraints on Pricing in Personal Markets and Use Numerous Instruments to Maximize Income and Maintain Down Enter Prices
The analysis proof is obvious that as well being care suppliers consolidate possession with different suppliers—for instance, a number of hospitals merging to kind a series or hospitals integrating with doctor practices—the costs paid for his or her care improve and insurance coverage premiums rise, with no commensurate improve within the high quality of care or improved medical outcomes. Well being care suppliers can extract larger income by means of unfair billing practices like facility charges, and thru numerous sorts of anti-competitive habits that improve the typical price of medical claims, thereby growing affected person out-of-pocket prices in addition to insurance coverage premiums paid by shoppers and employers. Anecdotal proof signifies that, so as to safe their place in plans’ networks, consolidated suppliers have required insurance coverage corporations to ensure the suppliers a minimal stage of income throughout some or all of an insurers’ traces of enterprise, and this will lead to further funds above the negotiated price for a subset of companies decided by the insurer.
In a aggressive market, well being care suppliers’ revenue motive wouldn’t essentially be problematic, as well being care purchasers vying for market share may exert downward strain on costs till an environment friendly equilibrium was reached. Purchasers are most frequently not in a aggressive market, nonetheless, and this isn’t solely due to horizontal and vertical integration amongst well being care suppliers. Supplier consolidation has been coupled with extra diverse sorts of consolidation of possession and monetary pursuits throughout well being trade stakeholders. For instance, insurers and TPAs have incentives to drive spending on claims upward, opposite to what a few of their purchasers might count on. As a result of their incentives are considerably aligned with these of suppliers, many suppliers and insurers see the revenue potential from integrating with one another as properly.
Insurers Have Monetary Pursuits in Conserving Well being Care Spending Excessive
Whereas suppliers typically have the market energy to demand and extract excessive costs, insurers even have incentives to maintain spending excessive. First, federal medical loss ratio (MLR) limits –– supposed to forestall insurers from promoting low-value plans –– have unintentionally contributed to larger costs: insurers make better earnings when supplier costs are larger underneath their totally insured plans. Second, in some circumstances, the insurer and well being care suppliers are owned by the identical entity, creating monetary incentives for the insurer to improve spending on these suppliers particularly. And third, main insurers have contracts with and typically share possession or different enterprise relationships with middlemen corporations that improve the insurers’ personal income and earnings as claims improve.
Many TPAs Have Monetary Pursuits That Are likely to Enhance Well being Spending, and Employers Have Restricted Selection in TPAs
Importantly, as a result of employers should not buying medical health insurance in a aggressive market, employers can’t “clear up” these issues or disincentivize excessive spending from insurers or suppliers. The TPA market administers well being plans for self-funding employers, and it’s dominated by the BUCAs (Blue Cross associates, United, Cigna, and Atena), entities which have their very own pursuits to extend monetary relationships and claims prices. Lawsuits introduced by employers and investigative journalism counsel that some TPAs then make use of methods hidden from employers – similar to “skip” lists, cost-plan offsetting, shared financial savings, and extra – to accrue billions of {dollars} in income on the expense of the employer, their staff, and a aggressive market. These opaque agreements between TPAs, suppliers, and middlemen are sometimes unknown or misunderstood by employers, the dominance of the BUCAs give even the biggest employers few possible options, and the TPAs present little data to employers about how their cash is definitely being spent.
Middlemen Make Cash by Repeated Adjudication of Claims and Larger Prices
Amidst these supplier, insurer, and TPA markets, middlemen entities have entered to additional maximize revenue for the opposite stakeholders and themselves. Whereas middlemen entities promise better effectivity and billing accuracy for his or her purchasers, the charges of this huge and fast-growing trade are subsumed in insurance coverage premiums and affected person out-of-pocket funds, and there’s rising concern of economic conflicts of curiosity and inadequate authorities oversight of their operations.
Middlemen are typically impartial with monetary pursuits tied to growing income for suppliers or insurers by means of a system of charges; typically middlemen are subsidiaries of one of many stakeholders; and typically middlemen are owned by non-public fairness corporations that additionally personal a number of different well being care stakeholders. Among the middlemen corporations contract with each insurers and suppliers, promising elevated income to each, and making a system of repeated adjudication between the completely different arms of the identical firm, profiting themselves whatever the end result, with the inducement being for larger billing and better numbers of disputes difficult the payments.
Whereas among the middlemen entities are long-standing members of the market, similar to RCMs, new sorts of middlemen emerge wherever market benefits might be discovered. Take for instance, HaloMD. This impartial dispute decision (IDR) administration firm arose solely after the passage of the No Surprises Act and the creation of the federal IDR course of. By dealing with the IDR course of primarily for suppliers –– by means of dispute submission, negotiation, provide evaluation, and extra –– these entities revenue from high-volumes of excessive fee dedication awards. And to date, HaloMD has been fairly profitable: throughout all disputes, HaloMD has secured a median award of 934 % of the qualifying fee quantity (a proxy for in-network charges). These IDR administration corporations, like so many different middlemen, have a transparent motivation to maximise reimbursement for suppliers, which is able to finally improve well being care prices and general spending.
Motion is Wanted: Left Untouched, The Complicated Net Will Proceed to Develop and Hurt Sufferers
An intricately complicated well being care monetary internet is undoubtedly driving well being care costs and mixture spending upward. Left alone to market forces, spending will proceed to climb, doubtless at accelerating charges. The heightened focus of well being care entities on possession and contracting relationships that improve income and profitability are more likely to take an more and more damaging toll on high quality and entry to needed care as properly. Creating efficient coverage options requires an understanding of the prevailing monetary incentives and the way they’re intertwined throughout stakeholders of varied sorts. As a result of the revenue motive is so robust and at the moment unrestrained in industrial markets, and since the monetary standing of the broad array of well being care entities have turn into so interdependent, no single incremental coverage technique will suffice to handle the results of the established order. Nevertheless, a set of coverage methods on the federal and state stage have the potential to constrain the present price development trajectory by eliminating perverse monetary incentives and disentangling the profit-driven relationships which have put insurers, suppliers, and their middlemen at the moment at cross functions to shoppers, employers, and governments.
The total skilled perspective is obtainable to learn and obtain right here.
