Proof from Canada, the United States and Europe exhibits that weather-related disasters aren’t skilled equally. The folks hardest hit are sometimes these with the fewest sources to manage.
Decrease-income and marginalized populations face higher publicity, have fewer sources to arrange or recuperate and incur the next proportion of losses not lined by insurance coverage.
Even when they’re insured, many individuals have issue masking the deductible as a result of they lack emergency financial savings. This implies injury isn’t repaired, folks dwell in unsafe or unhealthy situations and the monetary and private threat of future occasions is elevated.
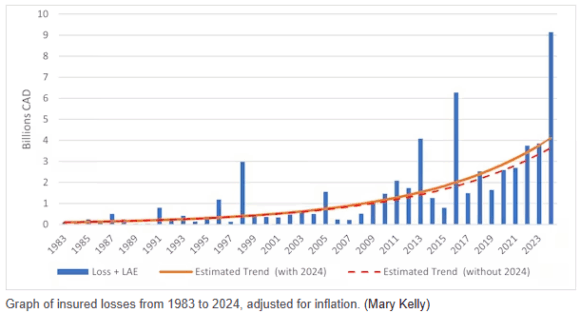
Insurance coverage helps households recuperate and might stop them from falling — or falling deeper — into poverty after a catastrophe. However throughout Canada, insurance coverage is turning into costlier and, in some locations, tougher to get. Between 2019 and 2023, common dwelling insurance coverage premiums rose by 21% total. For lower-income Canadians, that improve was 40%.
Widening Safety Hole
Canada’s rising insurance coverage safety hole is a critical concern, and it’s widening at a time when weather-related disasters are turning into extra frequent and extra extreme.
When households are uninsured, losses can pressure family budgets and go away folks unable to satisfy their fundamental wants. As excessive climate escalates, so does the chance that extra households will discover themselves unable to recuperate.
Affordability is the first driver of the safety hole, however it’s not the one one. Many Canadians don’t perceive the advantages of insurance coverage, or underestimate the chance and price of struggling a loss.
Accessibility to insurance coverage can be a problem, particularly in distant areas the place it’s often bought in individual. Whereas the expansion of digital buying channels helps, it’s not an answer for these with out dependable web or ample digital abilities.
Lastly, the market itself doesn’t all the time meet the wants of low-income or in any other case marginalized teams. There’s a lack of insurance coverage merchandise designed for these teams, leaving many with out the safety they want.
Strengthening Neighborhood Resilience
Higher insurance coverage choices, stronger investments in mitigation and higher assist for shoppers can assist scale back inequities and strengthen resilience.
Neighborhood-level mitigation is an effective place to begin. Land-use planning that steers growth away from high-risk areas can stop future losses. Packages like FireSmart, which reduces wildfire losses, and infrastructure designed for a altering local weather additionally assist restrict injury as extreme climate turns into extra frequent.
Nationwide assessments present that making housing extra resilient reduces publicity for lower-income and marginalized households which might be extra prone to dwell in older or poorly maintained houses, placing them at higher threat.
Whereas main retrofits may be expensive, even small upgrades comparable to bettering drainage, putting in backwater valves or fire-resistant supplies can assist stop injury. Many municipalities present focused subsidies and incentive packages that assist these upgrades, significantly for households dealing with higher monetary constraints.

Making hazard data simpler to search out and perceive may assist guarantee nobody is left behind when disasters strike. Many Canadians lack clear details about the hazards they face and learn how to put together for them. Some residents, together with newcomers and seniors, could face limitations in accessing or performing upon out there data.
Lastly, neighborhood helps can additional strengthen resilience. Folks with sturdy social ties and entry to neighborhood organizations recuperate extra rapidly after disasters. Packages that construct native networks and assist neighbourhood teams can assist accomplish this at a comparatively low price.
Closing the Safety Hole
A important step in decreasing the unequal impacts of weather-related hazards is closing Canada’s insurance coverage safety hole. Microinsurance is one promising resolution, and these simplified, low-cost insurance policies can present fundamental safety at a fraction of the fee for households that can’t afford conventional protection.
Embedded tenant insurance coverage — robotically included when renters signal a lease — is one other method that ensures fundamental protection.
Digital instruments, comparable to mobile-friendly sign-up platforms and plain-language coverage explanations, can scale back limitations for individuals who battle with expertise.
Public assist for income-tested premium subsidies or credit can carry important protection inside attain for low-income households, whereas community-based disaster insurance coverage — the place native governments or neighborhood teams prepare protection on behalf of residents — affords another choice.
Whereas Canadians can’t cease excessive climate, we will work collectively to stop it from worsening inequality. Rising consciousness, decreasing losses, closing insurance coverage gaps and constructing resilience are key to defending these at biggest threat.
{Photograph}: A employee walks in a devastated neighborhood in west Jasper, Alberta, Monday, Aug. 19, 2024, after a wildfire precipitated evacuations and widespread injury within the Nationwide Park and Jasper townsite. (Amber Bracken/The Canadian Press by way of AP)
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. The Dialog is an unbiased and nonprofit supply of reports, evaluation and commentary from tutorial consultants. The unique article may be accessed right here.